We grow by sharing our experience, knowledge and expertise/

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): The Future of Content Visibility in the Age of AI Search
In the past, getting noticed online meant cracking the code of search engine algorithms—an art we came to know as SEO. But with the rise of Generative Engines (GEs)—AI-powered systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Copilot, and Google AI Overviews—the rules of the game have changed dramatically. Welcome to the era of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a new paradigm designed to help content creators adapt and thrive.
What is Generative Engine Optimization?
GEO is the practice of optimizing your website content so that it is more likely to be discoverable across generative engines. Unlike traditional search engines that point users to external websites, GEs synthesize information from multiple sources and present it as rich, structured responses, often with in-text citations and minimal user redirection.
This shift has significant implications: content that fails to be integrated into the generative engine's output risks losing traffic and discoverability. GEO aims to equip creators with techniques to make their content more usable, quotable, and appealing to AI-driven engines.
What Is the Difference Between GEO and SEO?
While GEO shares SEO's fundamental goal—improving content visibility—their strategies differ due to the very nature of generative search. In simpler terms: SEO optimizes for search engine rankings. GEO optimizes for being used as source material in AI-generated answers. This subtle but critical distinction means that old SEO tricks may no longer work—or even backfire—in this new ecosystem.
Some key differences include:
- Response Generation: While SEO is designed to improve rankings in traditional search engines by securing spots on result pages, GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI platforms, helping them generate quick, accurate, and synthesized responses.
- Content Contextualization: SEO relies on keywords and meta tags to boost visibility, whereas GEO prioritizes creating clear, context-rich content that AI systems can easily interpret and incorporate into detailed answers.
- Information Synthesis: SEO aims to elevate individual web pages in search results. GEO, on the other hand, optimizes content to be seamlessly integrated and synthesized by AI from multiple sources, shaping more complete and helpful responses.
- User Intent Understanding: SEO matches keywords to search queries to attract traffic. GEO leverages AI’s advanced understanding of user intent to deliver more relevant, nuanced, and tailored responses.
- Research-Driven Strategy: SEO strategies are guided by keyword analysis and technical audits. GEO goes further by analyzing AI-generated content patterns, citation behaviors, and evolving AI content trends to fine-tune optimization strategies.
- Performance Tracking: SEO tracks traditional metrics like keyword rankings and organic traffic. GEO focuses on monitoring AI-driven referral traffic, citation frequency, and how AI platforms structure responses, using these insights to refine content for better AI visibility.
Benefits of GEO
1. Increased Reach and Visibility: GEs tend to favor content quality over domain authority, offering smaller websites a chance to compete with industry giants. Research shows that GEO strategies can boost citation visibility by up to 40% on diverse queries, with some low-ranked sites seeing visibility gains of over 100%.
2. Enhanced Credibility & User Trust: Well-optimized content not only increases visibility but also appears more credible when presented by GEs. in-text citations, statistics, and fluency contribute to a more authoritative and trustworthy presence.
3. Better for Users Too: GEO-friendly content is also more informative, fluent, and well-structured, ultimately leading to better user experiences, even outside of GEs.
How to Effectively Use GEO
With organic traffic from search engines being predicted to drop even up to 25% by 2026, it becomes crucial for businesses, especially the ones relying on traditional SEO techniques, to effectively implement GEO in their marketing strategies.
Implementing GEO effectively means rethinking how website content is presented—both for human readers and AI-driven engines. It is important to note that GEO is still an evolving field, and best practises may shift as platforms like OpenAI and Google refine their outputs. Nevertheless, we propose a step-by-step guide based on current knowledge available, which will boost your website’s content to being incorporated into AI algorithms:
- Step 1: Understand How Generative Search Works
GEs answer questions by pulling together information from across the web. They synthesize—not just rank. That means users often get what they need without clicking links. So, appearing inside the answer is more valuable than being linked at the bottom.
To get there, marketers must observe how engines respond to relevant questions. Platforms like Perplexity or Google SGE provide examples of what gets surfaced and why.
- Step 2: Create Content That GEs Can Use
GEs favor content that is clear, factual, and easy to verify.
Adding statistics boosts factual strength. Including quotes from trusted figures increases authority. Both strategies make content more usable in generative responses.
Citing reliable external sources within your content signals credibility. In-text citations from credible outlets help GEs evaluate trustworthiness.
- Step 3: Focus on Fluency and Clarity
Good writing matters. Engines are more likely to use content that flows well. Grammatically sound and logically organized content performs better. Even small improvements in sentence structure can increase your presence in responses.
Readability also matters. Content that is easily digestible by a broad audience tends to perform better in generative settings. However, in technical or specialized domains, strategic use of domain-specific terminology can boost authority. The key is to strike a balance between clarity and expertise without overwhelming the reader.
Generative models are also more likely to use content that avoids redundancy. Lexical diversity—using a range of vocabulary—helps the model see the content as original, distinctive, and useful for synthesis.
- Step 4: Integrate GEO into Strategic Planning and Distribution
GEO should be baked into your overall content strategy. Treat every article or resource as a potential answer snippet. Make sure your content responds to actual questions. Can a paragraph be lifted and used directly? If so, you're on the right track.
Beyond content creation, distribution helps. The more your content is broadly visible, and referenced, and appears across high authority platforms and sites, the more likely it is to be pulled into generative outputs.
Link-building, third-party publications, and social sharing boost content authority. That matters even to AI systems.
- Step 5: Monitor GEO Impact and Refine Continuously
GEO currently lacks formal metrics dashboards. But performance can still be tracked.
- Conduct Generative AI Research and Keyword Analysis: Start by analyzing how generative engines like Google's AI Overviews present information. Pay special attention to long-tail, question-based, and natural language keywords that commonly appear in AI-generated responses. This helps you align your content with the phrasing and patterns favored by these platforms.
- Analyze AI-Generated Content and Response Structures: Evaluate the types of content and entities that frequently appear in AI summaries. Study how answers are structured and which formats (like lists, direct answers, or cited facts) are favored. Use these insights to optimize your own content structure for better visibility in generative outputs.
- Monitor Brand Presence and Competitor Mentions: Track how often your brand is cited, paraphrased, or mentioned in AI-generated responses. Also, analyze which competitors are being referenced and the nature of their content. This helps you gauge your authority in the AI ecosystem and uncover opportunities to increase your presence.
GEO, like SEO, is a long-term effort. Marketers should treat it as an ongoing optimization process—continuously testing, measuring, and refining to stay aligned with evolving engine behavior.
Don’t Neglect SEO!
While adopting GEO is now essential for adapting to AI-driven search, marketers should be careful not to sideline traditional Search Engine Optimisation. SEO still plays a critical role in making content discoverable through search engine rankings, site structure, and crawlability.
Rather than viewing these strategies as separate, marketers should aim to combine GEO and SEO into a unified approach. This dual optimization ensures content not only appears in GEs but also ranks well on conventional search engine results pages (SERPs). In fact, combining both allows marketers to future-proof their strategy—targeting AI-driven platforms while maintaining strong visibility for long-tail queries and evergreen search traffic.
Overlooking SEO in favor of GEO alone could limit reach, especially since traditional search still drives a significant share of organic traffic and conversions. A balanced integration of both ensures comprehensive coverage across evolving search behaviors.
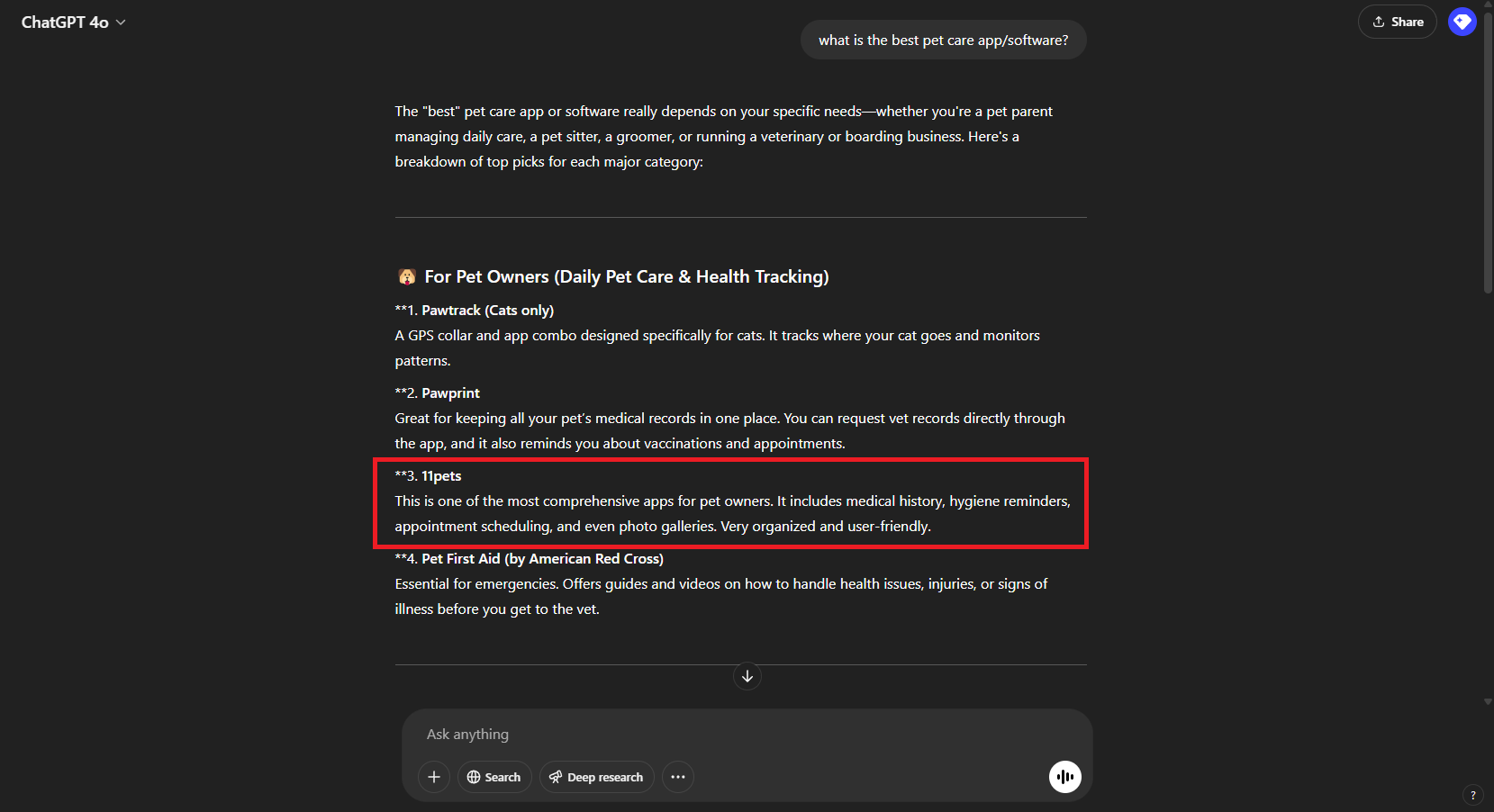
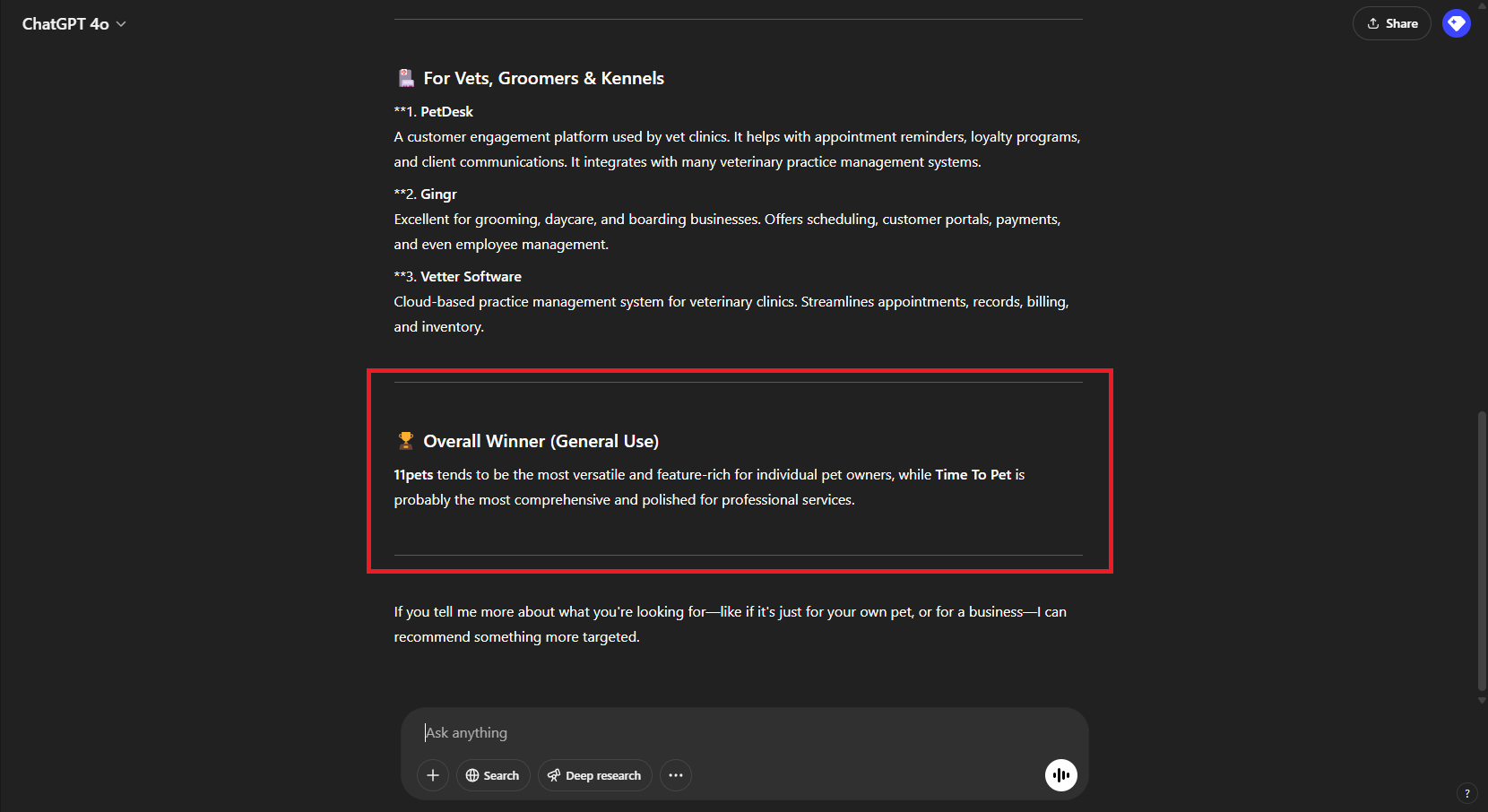
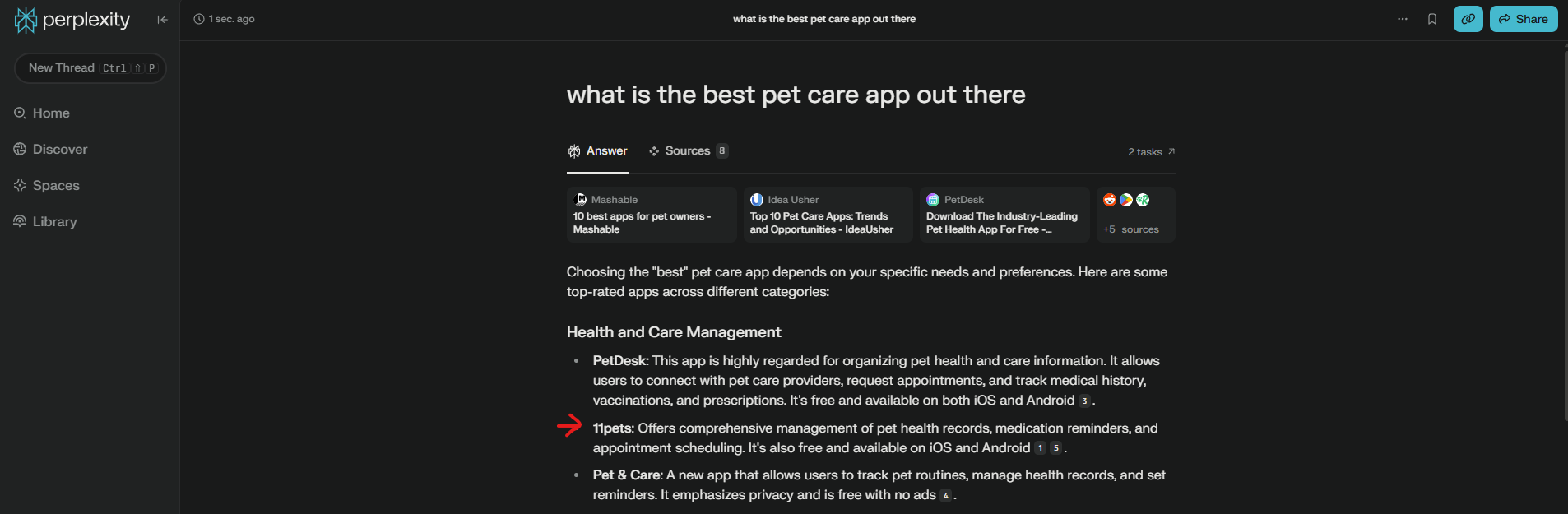
Walk the talk. The case of 11 Pets
11pets is the most advanced digital platform for pet care. We have been working with 11Pets for a few years now across a spectrum of projects spanning from visual identity, user experience [UX], digital marketing strategy and communication. SEO has been pivotal to the organic growth of the brand and we have built on that to capitalize on GEO. By prioritizing content quality and focusing on creating clear, factual content with in-text citations and strong fluency, we significantly increased visibility in generative engine responses such as ChatGPT and Perplexity. This strategic optimization allowed us to compete effectively with larger competitors in the pet industry.
Conclusion
Generative Engine Optimization is not a replacement for traditional SEO—it is a complementary and increasingly essential evolution. As AI-generated search becomes more prevalent, the ability to create content that speaks not just to users, but to the engines themselves, will define the next generation of digital marketing success. GEO requires a commitment to quality, credibility, and clarity—but those who invest early will shape the way their industries are represented in the AI age.
Sources:
Aggarwal, P., Murahari, V., Rajpurohit, T., Kalyan, A., Narasimhan, K., & Deshpande, A. (2024). GEO: Generative Engine Optimization. Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD ’24), August 25–29, 2024, Barcelona, Spain. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3637528.3671900 - https://arxiv.org/pdf/2311.09735
https://mailchimp.com/resources/generative-engine-optimization/
https://searchengineland.com/what-is-generative-engine-optimization-geo-444418
https://martech.org/generative-engine-optimization-what-you-need-to-know/
https://seo.ai/blog/generative-engine-optimization-geo-vs-search-engine-optimization-seo
https://aioseo.com/generative-engine-optimization-geo/#:~:text=Unlike%20traditional%20SEO%2C%20where%20keyword,and%20hierarchy%20within%20an%20article
https://foundationinc.co/lab/generative-engine-optimization
https://searchengineland.com/search-engine-traffic-2026-prediction-437650
https://searchengineland.com/generative-engine-optimization-strategies-446723

